Wouldn’t it be better if watching TV were more like browsing the Web, so you could pick the program you wanted to watch whenever and wherever you felt like watching it?
That’s one of the promises of IPTV.
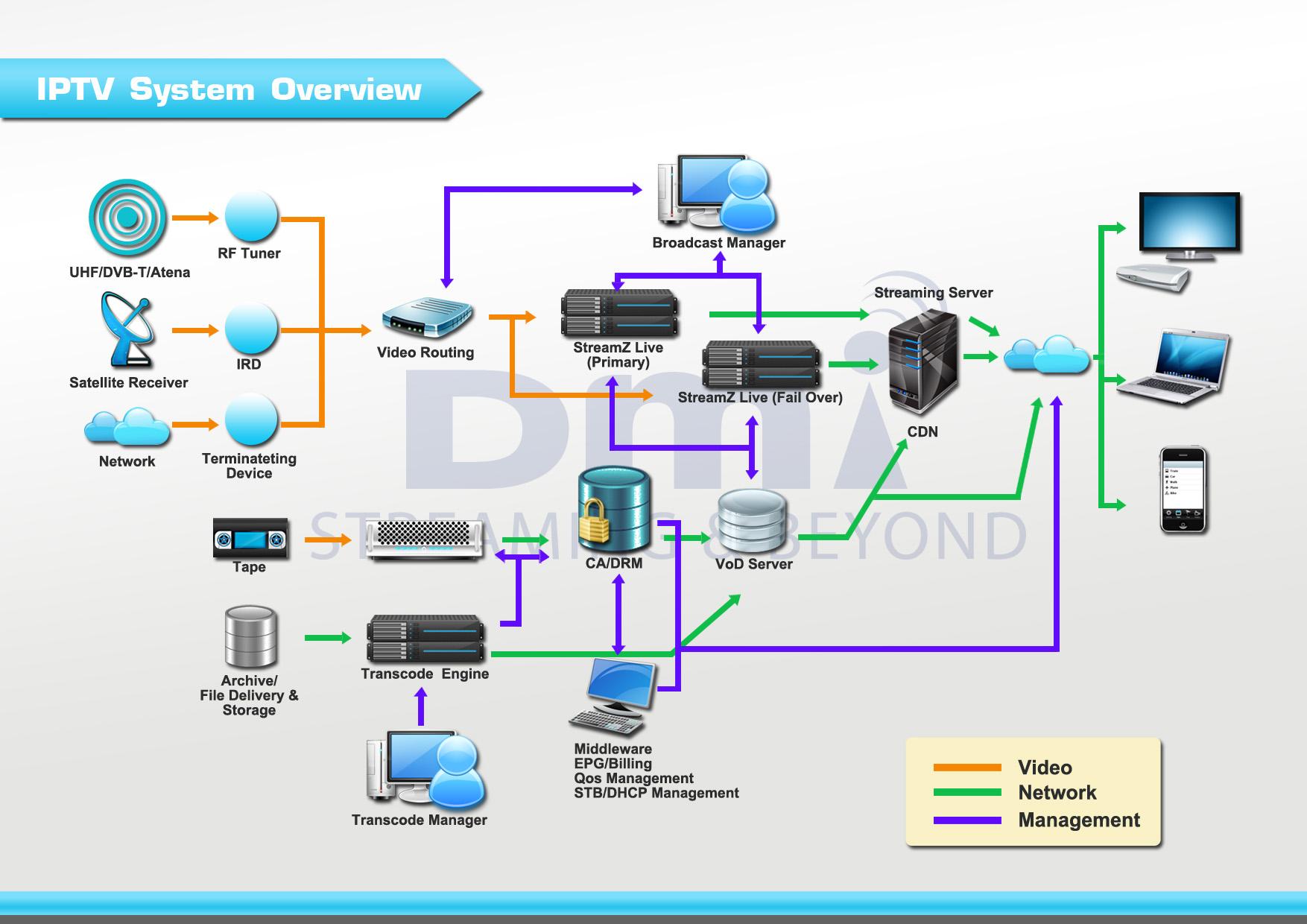
What is IP TV?
Internet Protocol television (IPTV) is the delivery of television content using signals based on the logical Internet protocol (IP), rather than through traditional terrestrial, satellite signal, and cable television formats.IPTV technology enables an organization to use an existing IP network to carry much more than just television. With IPTV, you can easily distribute terrestrial and satellite television and radio, videos, DVDs, digital Video on Demand (VoD), digital signage, information boards and web content throughout your facility.
Unlike downloaded media, IPTV also offers the ability to stream the source media continuously. As a result, a client media player can begin playing the data (such as a TV channel) almost immediately. You watch the program either on your computer or with a set-top box (a kind of adapter that fits between your Internet connection and your existing television receiver, decoding incoming signals so your TV can display Internet programs).
Three types of IPTV.
IPTV comes in three different flavors. All three forms of IPTV can work either using your computer and an ordinary web browser or (for much better quality) a set-top box and an ordinary digital TV.
- Video on demand (VOD).
Netflix (an online movie website), offers VOD. With such as service you select a TV program or movie you want to watch from a wide range, pay your money, and watch it there and then.
- Time-shifted IPTV
Here you watch watching ordinary, scheduled broadcasts at a time that’s convenient for you. An example is the BBC iPlayer. In the UK, the BBC (British Broadcasting Corporation) makes its last week’s programs available online using a web-based streaming video player called the BBC iPlayer.
- IP simulcasting
It is also called live IPTV. This involves broadcasting live TV programs across the Internet as they’re being watched.
How to view
Everyone who has a computer and a broadband Internet connection can watch IPTV, but most of us don’t want to watch television on a crude laptop screen. That’s why the future of IPTV is likely to involve viewers buying set-top boxes (sometimes called STBs) that receive input from your Internet connection (either via an Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi), decode the signal, and display a picture on your high-definition, widescreen TV. STBs are effectively standalone computers programmed to do only one thing: receive packets of streamed video, decrypt them, convert them back to video files (MPEG2, MPEG4, or whatever format they were in originally), and then display them as high-quality TV pictures. Apple TV works broadly this way, using a set-top box to run simple apps on a slimmed-down operating system (tvOS), which manages the process of streaming video via the Internet.
As a simple, more compact, and much more discreet alternative to a set-top box, you can use what’s called a dongle, which looks a bit like a USB flash-memory stick, but allows secure access to Internet TV programs. The dongle plugs into an HDMI (high-speed, high-definition digital video) socket on your TV and connects via Wi-Fi to the Internet to stream TV programs, movies, and music directly. Some dongles are entirely self-sufficient: Roku and Amazon Fire work this way without any help from a computer or mobile device. Google’s Chromecast is a little bit different: generally, you get it going with your computer, tablet, or smartphone (which effectively becomes a remote control), after which it directly streams your movie or TV program from the Internet.
What’s the difference between a set-top-box and a dongle? It’s pretty much this simple: a set-top system is a bigger box that contains a faster processor with more memory, so it can give higher quality video output; that makes it better for things like high-performance gaming. Some companies, such as Amazon and Roku, offer a choice of either a simple, relatively expensive dongle or a more expensive, higher-spec set-top box.
Benefits of IPTV.
- Cost-effective – Using your existing IP network, TVs, PCs, and AV display units without requiring a separate satellite/aerial signal distribution system within the building or campus significantly reduces cost with greater potential for high ROI
- Flexible and Scalable – Enterprise IPTV allows the addition of new TV and video sources and users anywhere there is a network connection without picture degradation, so it is quicker and less expensive to extend a system
- Rapid deployment – IPTV scalability and ease of management enables the rapid rollout of new TV, video and broadband services across the whole organization in response to needs and opportunities
- Save costly internet bandwidth – IPTV multicasting technology makes better use of LAN bandwidth, by streaming each channel once over the network regardless of the number of end viewers, rather than as multiple streams through your internet gateway
- Greater security – With IPTV systems, all internet access to streaming content can be blocked at firewall for greater security and regulatory compliance
- Extensive access control – Granular control of content access by user or group enhances security and regulatory compliance
- Stream content beyond the wired LAN – Recent technology advancements enable mobile consumers to keep up to date with the latest news, events and favorite entertainment channels on their chosen device, wherever they are
- Focus on the user experience – IPTV frees AV experts from mundane wiring concerns to concentrate on core competency: the user experience from source to display, e.g., content generation, digital signage, designing boardroom display systems or corporate studios
- Lower management costs – IPTV brings AV distribution under IT control for lower management costs and more efficient network planning
IP TV is the current and the future of television. And especially for the Hospitality industry (Hotels etc), it is must. With the rapid changes in media consumption, many hotels consider combining Internet and TV services, while at the same time hotel guests expect high image quality. Modern hotel guests, business travelers revere control and hence they must be given options.
Local available IPTV solution providers.
