THE IoT is a suite of technologies and applications that equip devices and locations to generate all kinds of information—and to connect those devices and locations for instant data analysis and, ideally, “smart” action. Conceptually, the IoT implies physical objects being able to utilize the Internet backbone to communicate data about their condition, position, or other attributes. Internet of things is a broad subject that spans many areas and has the possibility to be implemented in almost every workplace, building and vehicle.
The main reason why people are interested in this service is because it can produce economical savings, convenience, increased indoor comfort and a safer environment. By connecting sensors, meters and actuators to a network the user gets real-time information about the situation. The information is used for control, statistics and monitoring, resulting in possibilities for optimization.
According to the technology research firm Gartner, the Internet of Things (IoT) is the most hyped technological term in the world, above big data and cloud computing. The Internet of Things was first proposed by Kevin Ashton, a British technologist, in 1999 .There are several definition you can find for the Internet of Things from some major ICT vendors, service providers, and consulting firms.
Huge advancements in the fields of electronics and communication technologies over the last decade have increased the interest of Internet of Things (IoT). IoT is a combination of proficiencies and technologies emerging from various fields of knowledge. Computer programming, social science, informatics, Internet protocol, electronics and telecommunications are merged together to interlink the physical world with the cyber world. The economical value associated with cyber-physical systems is predicted to be massive, IoT alone has a total potential economic impact of 4-11 trillion dollar per year in 2025. The top end value is equivalent to about 11 % of the world economy.
Internet of Everything:
Internet of Everything (IoE) is a Cisco’s version to describe the Internet of Things. Cisco sees that this is not only about connecting the physical things, it’s about connecting things, people, processes, and data for making this planet smarter and greener.
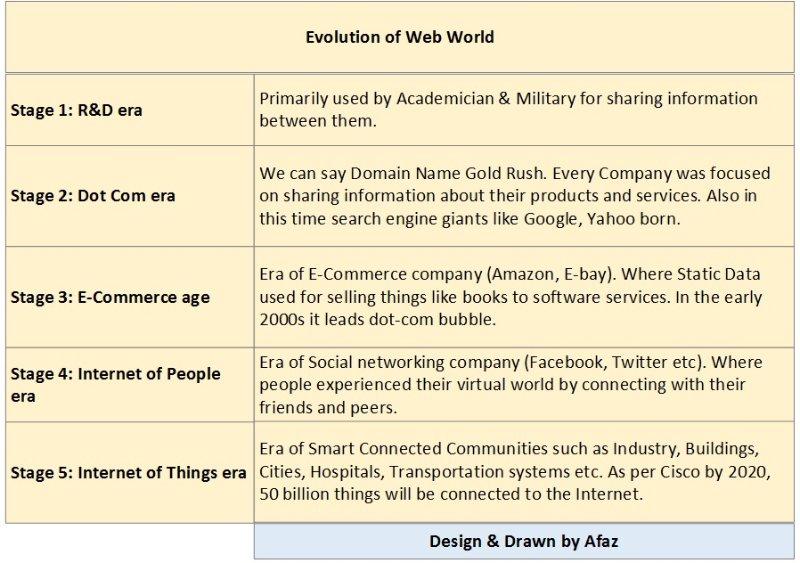
Evolution of Internet and Web World
The Internet has a wider meaning in our world; normal people classify Facebook, Google, Yahoo, etc., as the Internet. But in reality these are only web sites (http protocol based), they simply work in the application layer of the Internet infrastructure. A company like Facebook uses Internet infrastructure to send and receive data, and also to store information about users in a cloud or specifically in a data center located in some other geographical part of world. Web world has changed a lot in last 20-23 years, from some thousands to 5 billion mobile user.
According to Cisco’s John Chamber, the Internet of Everything is the fourth major evolution of web. By Cisco’s standards, the first phase of internet was connectivity, the rise of e-commerce was the second era, the rise of social networking companies is the Internet of People, which is the third era, and the Internet of things is the fourth major evolution of the web.
What Will We Do with the Internet of Things (IoT)?
For most people, the Internet means searching something in the Google search engine, which searches the database of 4000 exabytes of Information. We created the Internet only 20 years back and it has already become 4000 exabytes in size (4000 exabyte is roughly equivalent to a round trip distance to Pluto from Earth, multiplied by 80). Every connected machine will create a big chunk of data in IoT world. What will we do with this much data? And how will this affect our life?
With IoT architecture, we can connect any physical things, monitor, control, and manage those things from anywhere in the world.
Why Is Now the Time for IoT? Enablers of IoT
The Internet of Things is not a futuristic, aspirational technology trend. It’s here today in the devices, sensors, actuators, cloud infrastructure, and business intelligence tools, such as IP-enabled building automation systems what we are using in Smart Buildings environment.
Internet of things creates more data than ever; tiny machines working in a fan of an HVAC system creates more data than a normal human does in a year. According to Microsoft, “Instead of thinking about the massive amount of data being produced, think about how one piece of data can provide value to your business.”
Unlike earlier efforts to track and control large systems, such as radio-frequency identification (RFID), the Internet connection gives this shift almost limitless versatility.
A number of significant technology changes in the last couple of years enables the rise of the IoTs. These include the following
Why Is IoT Regarded as a Fourth Industrial Revolution?
According to consulting firm Goldman Sachs, the Internet of Things can be broken up into five key verticals of adoption: Connected Wearable Devices, Connected Cars, Connected Homes, Connected Cities, and the Industrial Internet.
From the figure below, you can understand that IoT will be implemented in almost every industry verticals. IoT will change the traditional industries like Mining, Metal, Oil & Gas, Transportation, Chemical etc.
The German government saw this as an opportunity and made a strategy to use the Internet of Things as a backbone for changing their economy. They regard the Internet of Things as the next big thing and refer to it as a fourth industrial revolution. German researchers and analysts predict that it has the potential to be equivalent of industrial revolution in 21st century.
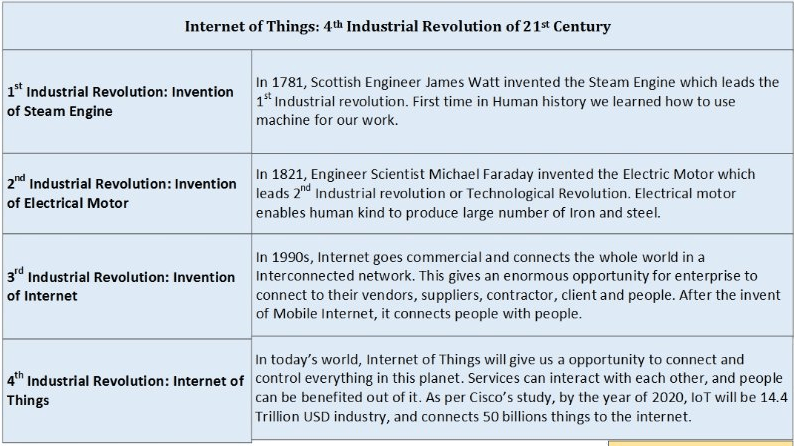
You can imagine the importance of the first three industry revolutions in the history of mankind. Some people say this is ridiculous: How can we match the importance of first three revolutions? In 1992, during early days of the Internet, people also never imagined about the present value of the Internet. Nobody ever imagined that e-commerce companies like Amazon will sell everything from groceries to software in a virtual store.
Traditional Industrial companies like Rockwell Automation, General Electric, and Schneider Electric are working with ICT leaders to optimize the operation cost of manufacturing, oil and gas, mining and metals, and the medical industry. IoT is bringing and collaborating on traditional operational technology (OT) and process engineering to information technology. So you can imagine that IoT will create millions of skilled and unskilled jobs, just like the previous three industrial revolution.
According to Cisco Systems research, by the year 2022, the economic impacts of IoT systems can reach up to $14.4 trillion.
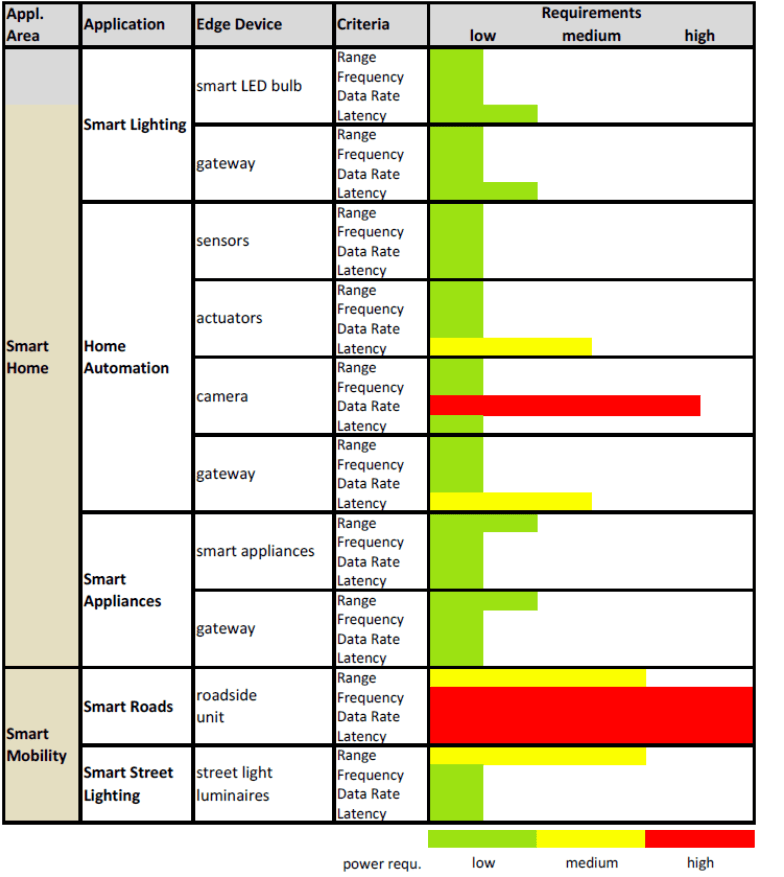
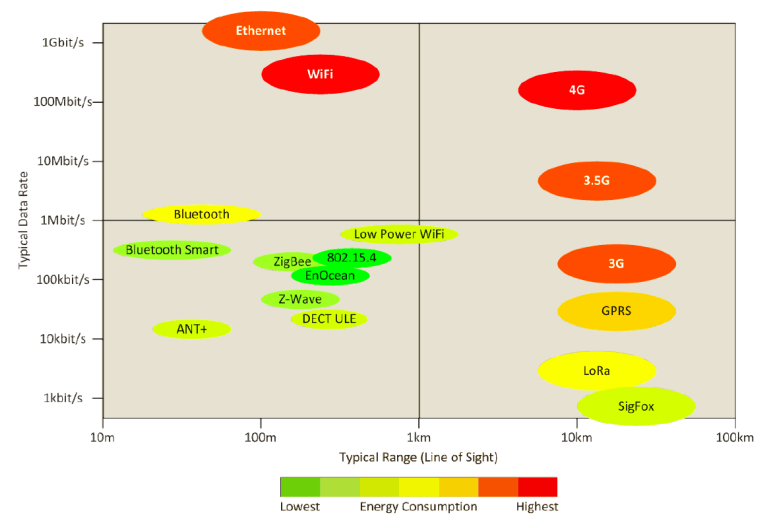
IoT systems uses many different types of communication technologies including Wifi, 3G, Ethernet, Bluetooth, LoRa etc. The main technical criteria for choosing a communication technology for a specific purpose are presented below.
• Range: The furthest device must be able to reach the gateway or access point with information. The range of communication technologies span between 10 m and 100 km.
• Frequency of communication sessions: How often the device have to send information. Monitoring devices sends information constantly whereas maintenance devices only send information a couple of times a day.
• Data rate (bandwidth): The amount of data that has to be transmitted determine the data rate. An actuator might only need 1 bit/s whereas a live video streaming service needs up to 10 Mbit/s.
• Latency: The latency determine the reaction time after an external trigger sends a signal to a device.
Devices which have a high performance in these criteria tend to use more power than other devices. To minimize the power usage a technology should be used that is “just enough” for its purpose. The power requirement for home and road devices is shown in figure below.
Types
IoT-systems demand certain type of communication depending on their appliance, like high data rate or long range connection. In figure below some conventional communication types is presented with the power demand needed for respective type.
General Applications
Internet of things is a system of sensors and actuators connected by networks.
These systems can monitor and manage health and actions of connected object and machines. There is no limitations of where IoT-system can be implemented.
The most promising appliances of IoT-system has been categorized in the following sections.
Human
IoT has a great potential for increasing wellness and human health. Devices that are attached to or inside the human body can continuously monitor patients in everyday life. IoT linked with the human body have also the possibility to improve productivity and performance in the workplace .
The use of IoT technology to monitor and manage human health and fitness is already in use in form of fitness trackers and smart watches. Interoperability between this information and other information about the user could potentially detect health problems.
Home
IoT in homes can be applied to energy management, maintenance, security and domestic chores. The latter is the segment where it’s estimated that the most profit can be made. It’s estimated that IoT can reduce workload in homes such as vacuuming, cleaning, washing, preparing food, gardening, etc. by 17 % [1].
Using IoT in homes to control thermostats, ventilation and electrical use is estimated to save 20 % on energy consumption [1]. IoT-systems applied in homes can greatly increase safety and security. Monitoring the home can reduce the losses due to break ins, fire, water leaks and injuries.
Retail environments
Physical spaces where consumers engage in commerce purchasing goods or services is defined as retail environments. This segment has change significantly the last past two decades due to internet and the rise of online shopping. IoT can be implemented so that customers can be guided with smart phones to the right product or for the store to optimize store layouts. Another possibility of IoT applications is fully automated checkouts where costumers simply walk out of the store with the product.
Offices
Offices has similar appliances as in the home, managing energy and security systems. However the office has a higher energy consumption due to the high power demand of machines and cooling. IoT can optimize the office productivity by tracking activity and interactions.
Factories
IoT has a critical role in digitalizing the processes in factories. Optimization of operations and inventories is of great value for the companies. However both predictive maintenance and safety is also of considerable importance.
Manufacturers can gain a comprehensive view of the whole production and make real-time adjustment to the process and avoid defects.
Vehicles
Service, maintenance and design is the main applications of IoT on vehicles. Vehicles include cars, trains, truck and aircraft. IoT is estimated to reduce maintenance spending by 10-40 % and reduce delays due to mechanical issues by 25 %. Cars are getting more digital each year and an IoT-system is the next step
for a modern car. IoT can greatly increase the comfort by providing maintenance recommendations, apps for real-time traffic data, tracking lost/stolen cars or improve safety and reliability.
Worksite
IoT appliances on Worksites can generate lots of value, both economical and health-wise. Worksites is defined as oil and gas exploration and production, mining, construction etc. Work that is done outside in constantly changing, unpredictable and dangerous environments. Repairs, breakdowns or maintenance
can keep machinery out of use for 40 % of the time making IoT incredibly valuable.
Every worksite have to adapt their own kind of IoT-system depending on their process.
Construction site
IoT can be implemented during the construction of buildings. As explained in the worksite section the construction site can be optimized by giving information about equipment, progress, availability and maintenance. The main function of IoT application in construction sites is the possibility to ensure that the building is dry, have an appropriate airflow in the ventilation and that the heating system is
calibrated.
Cities
IoT initiate possibilities such a “smart city” that can improve services, making traffic smoother, conserving water, reduce energy usage and improve quality of life.
It is estimated that 3.7 million deaths in 2012 were linked to outdoor pollution.
IoT can provide cities and citizens with real-time data where air is polluted and how to decrease it [1].
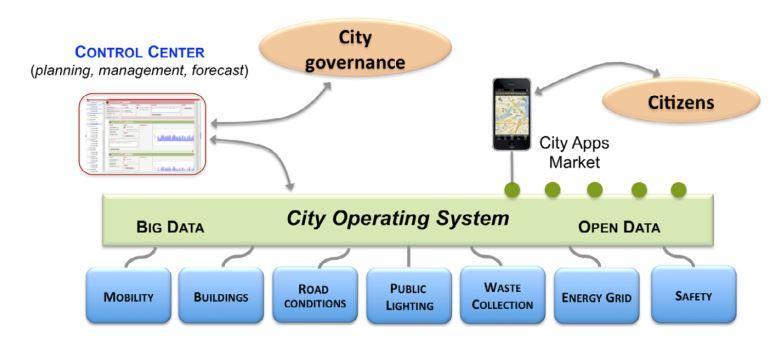
The city governance could control roads, lighting, waste collection etc. depending on citizen needs as described in figure below.
IoT applications in the building services sector.
Designing building services is an important aspect of building construction. Much knowledge is needed in order to produce a robust system that consider safety, efficiency and budget. The systems must be constructed so that maintenance and adjustments can be performed.
The development of IoT increases the need for building services to take IoT into consideration when designing. The following section reviews the possible IoT appliances in buildings related to building services.
A majority of the potential appliances correlates to automation of systems because the main use of energy related IoT appliances is the possibility to do actions before something take place instead of after.
- Occupancy managed heating system
It’s important to keep a low indoor temperature without creating a dis-satisfactory indoor climate in order to achieve a low energy consumption.
Modern offices are using regulators to control temperature in rooms depending on occupancy. This technique is rarely used in homes but it has the potential to lower the energy consumption. By utilizing IoT to gain perfect occupancy detection the heat and airflow can be turned up and down
depending if the person is on the way home or leaving.
The speed of which the temperature is lowered depends on the volumetric heat capacity, the transmission losses and ventilation losses. Similarly, the speed of which the temperature is raised depends on the installed heating power. A building with a low installed heating power require a longer time to raise the temperature to a desired value. This means that the materials in the building and the installed heating power determine the lowest temperature the indoor temperature can be lowered to if the temperature is to be capable to be raised to a desired value in a specific time interval. - Occupancy managed ventilation system.
As well as the heating system the ventilation system can utilize IoT to lower the energy consumption and increase the indoor climate satisfaction. The VAV type of ventilation is scarcely used in homes but has the potential to lower energy consumption if used correctly. IoT enables occupancy detection
which can be utilized by the ventilation system. The ventilation can be set
to only partly ventilate the building when nobody is home and to lower the
heating needed for the supply air. - Energy management system
Individual apartments and homes can be equipped with an energy management system to see statistics about energy consumption. The energy consumption behavior of citizens is effected when they get reminded about energy savings and the costs of their consumption in real-time. The user has the possibility to receive information and alarms in the phone, such as abnormalities, leakages and general statistics. - Lighting control systems.
Lighting control systems in buildings is already available on the market and can be controlled using smartphones or tablets. The application lets you remotely manage lights that needs to be lit, their light intensity and their color. The introduction of IoT makes it possible for automatic personal adjustments for lighting. Lights can be set to automatically turn off when you leave the house and turn them on on return. Settings like ’night mode’ uses dimmers to illuminate paths if necessary in the middle of the night. A security mode can simulate human presence inside a house when no one is
home to mislead robbers [19].
• Control of electrical equipment and outlets.
Standby electricity use is defined as the electrical energy consumed by electrical appliances when they are turned off or not in use. Old electric equipment in homes today have a high standby power usage that constantly consumes energy. Standby energy consumption can be greatly reduced by controlling the outlets with IoT appliances. - Waterflow surveillance
IoT can be implemented in fresh water pipelines and buildings to determine leakage. The system can detect flow and send an alarm to the user if something is wrong. This technology is interesting in arid climates where fresh water is essential and in buildings where a water leak can cause severe damage.
One of the most common expenses for insurance companies is the damage caused by water leakage in buildings. The development of IoT raises the accessibility for a more commercial water leakage detection which further is going to increase the demand from insurance companies. Either the insurance is going to cost more for clients without waterflow surveillance or the insurance companies will simply put a demand to install these sensors or the clients will not be able to get an insurance on their building. - Security, surveillance and alarm systems.
Security and surveillance is becoming more accessible on the market with the expansion of IoT devices. The IoT devices in a homes can determine presence and send alarm to the user if something is wrong. Cameras can be installed that is turned on by occupancy detection and records the activity sending an alarm to the user that then can view the video from his or her smartphone. The possibility for IR-cameras to automatically determine the amount of people in a room enable a better fire safety management. Many pubs, clubs and other crowded area have a restriction on the amount of people that can be present and by monitoring the number of people visiting the owners get a better control over the fire safety. - Passage management.
There are already electronic locks on the commercial market which is controlled using RFID, fingerprints and Bluetooth, however IoT enables the possibility to remotely open and close doors using the cloud. The management of doors is interesting for facilities such as airports, hospitals, malls etc. for security reasons and fire safety. - Sanitation.
Cleaning and waste collection in huge facilities such as malls, airports, industries etc. can be a tedious task to perform. Keeping statistics on how often the restrooms are used and which bins that are ready to be changed can optimize routes for cleaning. A more optimal cleaning process results in economical savings and a better working environment. - Plant watering management.
A great deal of money and time goes into watering plants in buildings such as universities, malls, airports, etc. and IoT enables a more optimized approach.
A fully automatic watering system is difficult to accomplish considering the multitude of pipes that has to be installed, however, a sensor can inform the user on how much water and nutrition that is left in the pot. The information can then be used to optimize routes and schedules. - Energy storage and management in homes
Residential heat pump is a common energy saving technology that supply buildings with cheap heating. A more digital home can optimize the usage of heat pumps and other energy generating equipment such as solar collectors, solar cells, wind turbines and batteries. The whole energy system can be
optimized to heat the water in the morning and evening when the demand is the highest and to use electric equipment such as the heat pump during the night when the electric cost is low. - Identification of customer movement in shopping areas.
Determination of customer movement in shopping areas is not only interesting for maintenance but also for advertisement. A crowded path in a mall is obviously going to be the most lucrative spot to place advertisement and companies are ready to pay extra to advertise in these areas. Shopping mall owners could monitor costumer movement to charge extra for advertisement in these areas making it an interesting concept for a more digital shopping structure. - Facility management and maintenance.
Companies working in facility management and maintenance works constantly with supervision of real estate. These companies often supervise ladders, playgrounds, roofs, ventilation aggregate, filters, fire safety equipment, etc. which is a very time demanding task. IoT offers the possibility to significantly lower the routine control of buildings by installing sensors that can verify the condition of devices instead of an operating technician.
Safety, security, privacy and integrity
IoT systems regularly exchange sensitive information throughout the network and the biggest challenge with IoT today is to secure the information. Security mechanisms have to be developed in order to minimize the risks. Examples of these security mechanisms are protocols, network security, identity management to achieve authentication and authorization to assure that the data is seen by the right user, trust between entities and user interaction, and lastly fault tolerance to prevent and detect attacks. The most difficult attacks to avoid is physical damage, eavesdropping or node capture. Node capture is done to extract information and controlling entities .
Security depends greatly on how often the sensor sends information. A considerable amount of sensor information is needed to break a secure system.
This results in a sensor that sends information once an hour is much more secure than sensors that sends information every second].
Risk analysis is often done to provide the user with information about the security. A reasoning strategy for improving the security in IoT-based smart home environments is a method based on three components: the feasibility of conducting an attack, the attractiveness of the system, and the damage caused by an attack.
The first two factors provide the likelihood of an attack and the third help to weigh the overall risk.
A safety concern with IoT is the topic of who is the owner of the information and were it may spread. A device might belong to a company, sending information through a network to a server, the data is then treated by an application belong to another company. The application company might have an interest in the data for other uses like personalized advertising. This problem can be divided in three methods: Only the company may see the information, this greatly limits the possibility for interoperability; everyone can use the data, this encourage competition of the application companies and greatly increases possibility for interoperability; the last method is to seek an agreement regarding sharing
information with external companies.
The necessity of connecting personal belongings and information to the network will be increased as IoT is developed. The increased amount of personal information in the network raise the risk of identity theft and other frauds. As the data is becoming more and more sensitive, the demand for trusted devices will increase drastically.
References;
James Manyika. The Internet of Things: Mapping the value beyond the hype.2015.
IBM’s definition and business forecast about Big Data: http://www.ibm.com/big-data/us/en/
McKinsey Big Data: http://www.mckinsey.com/insights/business_technology/big_data_the_next_frontier_for_innovation
Cisco’s IoE website: http://internetofeverything.cisco.com/
Cisco’s Futuristic initiative: http://www.cisco.com/web/tomorrow-starts-here/index.html
Zebra Technology’s acquisition of Motorola: http://www.rfidjournal.com/articles/view?11682/
Security concerns about IoT: http://www.cisco.com/web/solutions/trends/iot/security.html
4th Industrial revolution: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourth_Industrial_Revolution